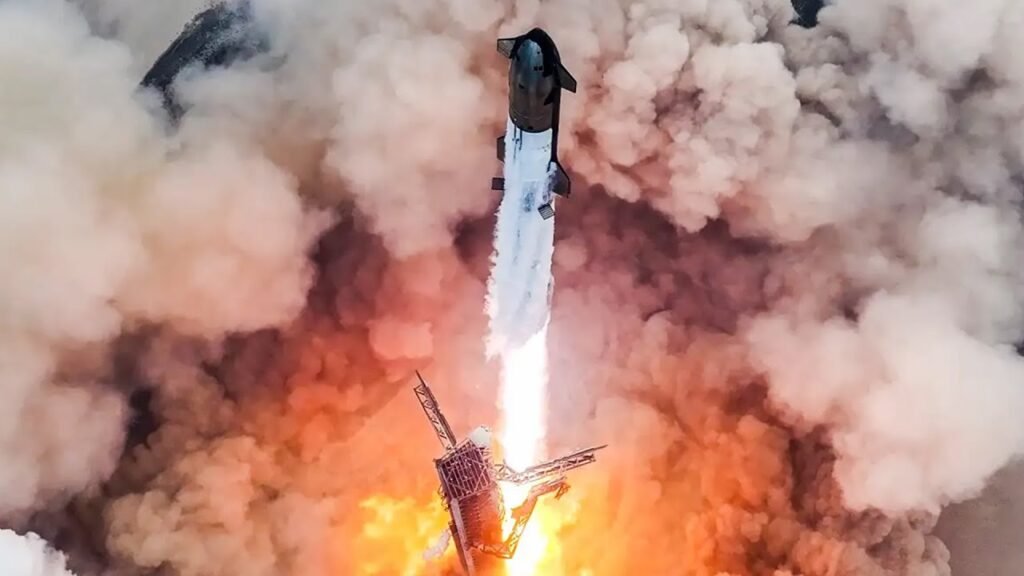
SpaceX is gearing up for the seventh test flight of its Starship rocket, set to launch from Starbase, Texas. This crucial mission will test new upgrades that are key for the future of space exploration.
Key Upgrades for Starship
| Upgrade | Details |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Propulsion | 25% more propellant for longer engine burns, supporting deep space missions. |
| Satellite Testing | Simulated Starlink satellites will be deployed during the flight to test deployment systems. |
NASA’s Role in Starship Development
NASA has contributed nearly $3 billion to develop Starship as part of the Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon by 2027.
| NASA Contribution | Details |
|---|---|
| Investment | $3 billion to support the development of Starship for lunar missions. |
| Mission Start | 2027, Starship will serve as a lunar lander for Artemis. |
Super Heavy Booster Precision Landing
SpaceX will test its Super Heavy booster with the Mechazilla landing system. This includes catching the booster using robotic arms. Additionally, a Raptor engine will be reused for the first time, marking a significant step in cost reduction and rapid reuse.
| Test Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Landing System | Mechazilla’s robotic arms will catch the booster mid-air. |
| Engine Reuse | First reuse of a Raptor engine from a previous mission. |
Starship’s Role in Mars Mission
Elon Musk’s vision for Mars exploration revolves around Starship. Designed for long-duration missions, Starship will be central to human exploration of Mars, the Moon, and beyond, with rapid reusability playing a crucial role.
| Vision | Details |
|---|---|
| Mission Focus | Starship will support long-duration missions to Mars and the Moon. |
| Rapid Reuse | Reusable spacecraft and boosters to drastically reduce costs. |
Starfactory for Mass Production
SpaceX is building a “Starfactory” at Starbase, a mass-production facility to manufacture hundreds of Starships each year, ensuring scalability for future space missions.
| Facility | Details |
|---|---|
| Starfactory | A facility at Starbase to mass-produce Starship vehicles annually. |
| Purpose | To enable the production of hundreds of Starships for future missions. |
Future Milestones for Starship
Starship must complete several critical milestones before it can support long-duration human missions, including:
- Achieving Orbit: Starship must successfully complete a full orbit.
- In-Orbit Refueling: Testing rendezvous and refueling to support long-term space missions.
| Milestone | Status |
|---|---|
| Orbit Achievement | First successful orbit remains an essential goal. |
| In-Orbit Refueling | Testing refueling in space for deep-space missions. |
Watch the Test Flight Live
The January 16 test flight will be streamed live on SpaceX’s website and social media platforms. This flight will provide essential data for upcoming missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.